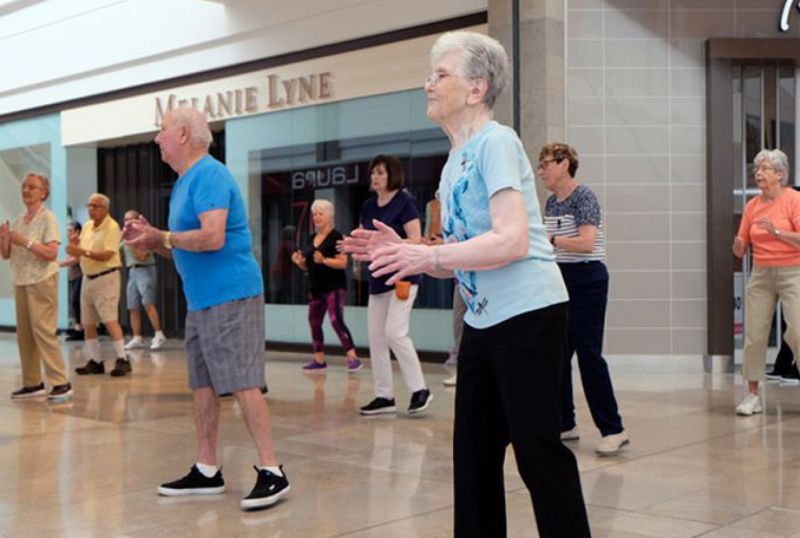The Untapped Potential of Retail Therapy
Retail therapy is the idea that shopping is a comfort-seeking escape from our everyday lives, a social or self-indulgent pleasure that makes us feel good. We’ve all experienced the welcome distraction of browsing a great store, or the rush of excitement we feel after purchasing a new pair of shoes or the latest smartphone.
Should there be more of a focus on this therapeutic nature of retail? Should customers come to understand the emotional benefits of shopping and seek it to regulate mood like they might a yoga class?
Brands must now view their stores as spaces that can improve the wellbeing of customers or even provide social wellbeing as a by-product? This focus can reinvigorate the role of the physical store and re-energise shopping as an activity. Research around the positive emotional impact of shopping has focused on the power of choice or the influence of self-satisfying purchases. Notably, this considers the moment of transaction the most fundamental part of the retail experience. But what about experiential retail? Does today’s role of the store open opportunities for greater impact on the wellbeing of shoppers? The role of the retail store has seen such evolution over the past decade. The types of shopping missions that exist have expanded beyond the functional. We now see people motivated by social, educational, entertainment and escapist shopping missions. Now that we have uncovered the power of these missions in retail, we have expanded our capability to provide more positive experiences.
What do we mean by wellbeing?
Wellbeing has become a commonly used term, being uttered by brands, media and in social discourse. What do we mean by wellbeing in this discussion? Do we mean happiness? Do we mean mental health? Not quite. Wellbeing is essentially our personal evaluation of our individual lives, referred to as ‘subjective wellbeing’, and it encompasses two components. The first is ‘cognitive wellbeing’, often measured by a global assessment such as 'how satisfied are you with your life?’. The second component focuses on emotions, referred to as ‘affective wellbeing’, assessed by measuring levels of positive and negative emotions throughout the day. While both are subjective measurements, cognitive and affective wellbeing have different applications over time. Our emotions oscillate and can be influenced by small moments. Yet life satisfaction (our cognitive wellbeing) is a more complex assessment and less easily shifted, rarely determined by a single moment. Our discussions about the influence of retail design concern ‘affective wellbeing’, the subjective measurement of positive or negative emotions.
Why is wellbeing something to consider?
Brands with a retail presence are increasingly associating themselves with causes such as social equality, inclusion and diversity and sustainability. Businesses realise the potential impact they can have on social issues, while also creating a stronger connection with customers through a shared value system. In this regard, wellbeing can serve a similar function. As an extension of mental health, wellbeing is one of the most significant social issues that remains largely untouched by global retail brands. There is no doubt it is an issue that holds immense currency with many consumers, so how can retail brands play a part in improving society’s wellbeing? If we assume that a retail store can enhance the wellbeing of a shopper, albeit fractionally, is this significant enough to justify motivation on the retailer’s part or even a sense of duty?
Wellbeing is determined by many accumulating variables, these include income, personal goals, gender, family, social relationships, employment, personality and genetics (there are many more). There is no one determining factor, making any small effect significant. In this sense, any momentary improvement in our mood should be considered worthwhile. This is similar to other social issues retail brands address. No single store or global business will have a sizeable environmental impact through their sustainability practices. Yet, despite this, retailers are beginning to understand the urgency and value of small, collective change in tackling these problems. Retail’s influence on social wellbeing is no different.
Retail therapy is not therapy retail
Retail therapy is not about a product or service that may improve wellbeing, but about the accompanying store experience. It’s important to differentiate between the two. Many retail businesses sell products aimed at improving wellbeing. Health and wellness is a growing retail market segment; examples include beauty products and services, electronic massage devices, holistic spa treatments or supplements, food and beverages. These products may benefit our wellbeing but are separate from the retail experience that accompanies them. Indeed, one may detract from the other. The stress-relieving benefits of a massage or facial may be reduced by a changing room lacking privacy, an unhelpful staff member or a payment process that takes the joy out of what was a pleasurable experience. Retail therapy focuses on store experiences with detachment from product or service benefits. The activity of shopping for clothes, shoes or a new phone could be an experience that alleviates stress or momentarily improves wellbeing.
How can the physical store experience improve the wellbeing of shoppers? Below we have identified several perspectives surrounding wellbeing that should influence retail design.
Retail is leisure that allows us to escape
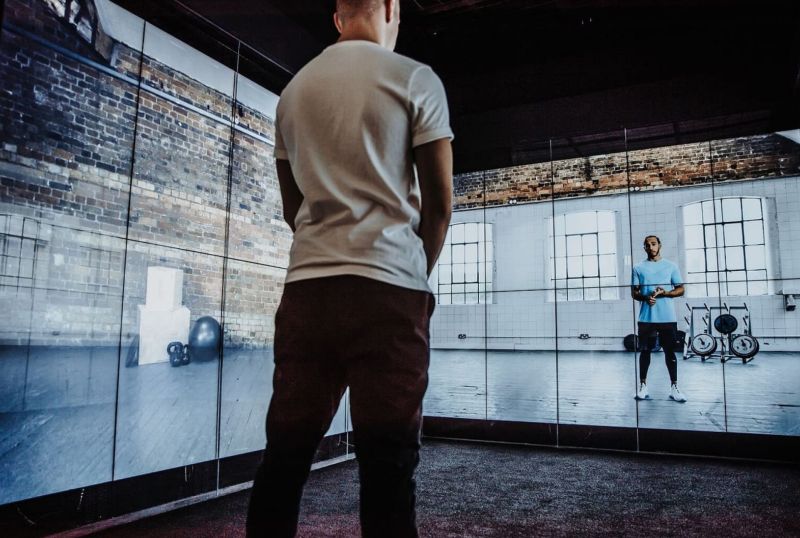
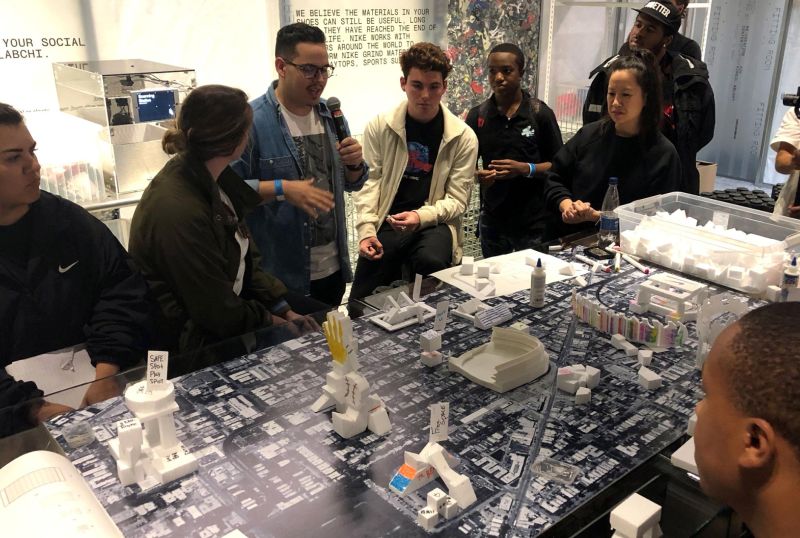
Many people need an outlet to escape the stresses and expectations of modern working life. This could be one of retail’s greatest contributions. A study featured in the Journal of Occupational Health Psychology found that psychological detachment from work (‘switching off’ mentally) is a major factor in improving wellbeing. Psychological detachment implies a distraction from job-related thoughts, something that prevents us from ruminating outside of work. Importantly this study found that frequent short-term periods of detachment were effective, as opposed to long-term holidays usually associated with unwinding from the stresses of work. Leisure activities providing short-term detachment after work improved wellbeing levels measured at bedtime, which can compound into better quality sleep, further improving wellbeing. Can visiting a retail store after work provide this psychological detachment and improve wellbeing? Psychological detachment is not achieved by time away from work, but by something requiring our attention aside from work. There is no doubt that a retail experience can provide this required escapism within each one of the functional, social, educational and entertainment consumer shopping missions.
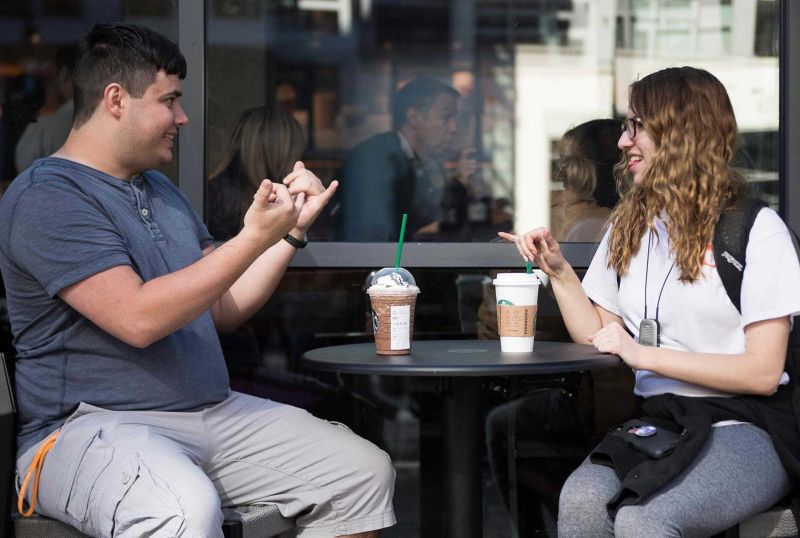
The importance of retail as social leisure
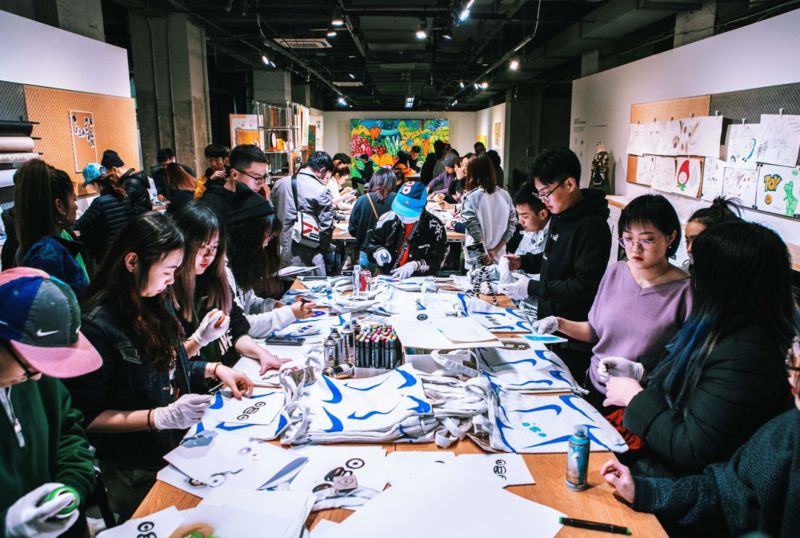
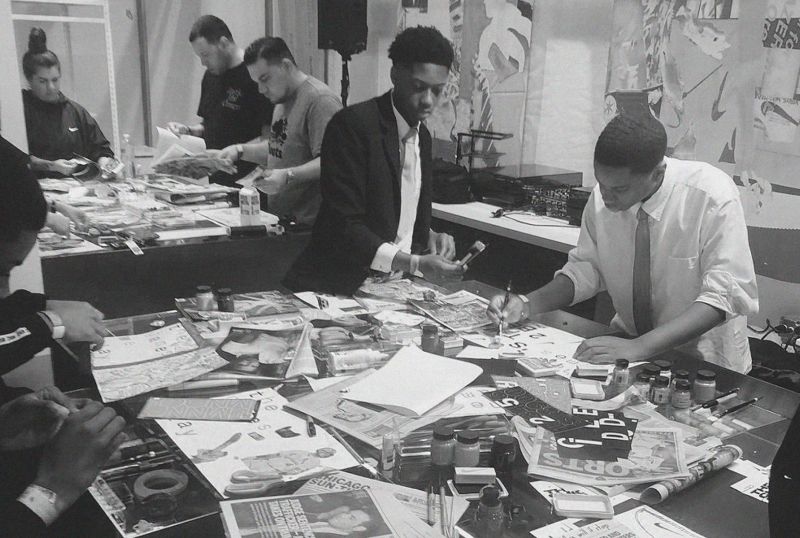
The psychological benefits of social interactions and social leisure are well known. Informal social activities, such as conversations with friends or participation in community activities, have a greater positive impact on wellbeing than solitary leisure activities. Psychologist Robert Putman, in his novel Bowling Alone: The Collapse and Revival of American Community, documents how an increase in solitary leisure time in America since the Second World War has caused a decrease in community trust and reciprocity. There is no doubt participation in social leisure benefits our wellbeing. Shopping has always been a social activity for some people, but more can be done to encourage shopping as a social pastime. Retail brands can provide more opportunities for social leisure by intentionally facilitating these experiences in stores. Facilitating social experiences is how retailers will provide a more enjoyable customer experience. Professor Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi, who is noted for his work on happiness and the psychology of optimal experience, found that people report social experiences with friends or family the most positively.
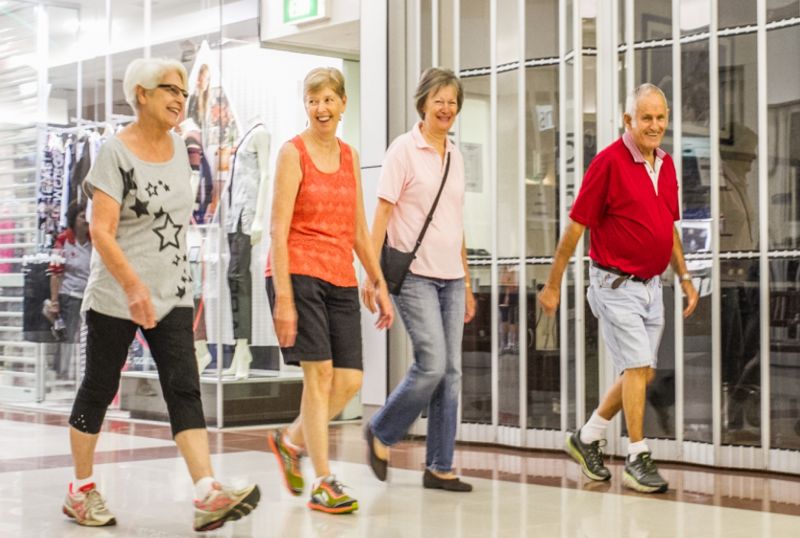
The social benefits of retail are especially pertinent for the elderly. Younger members of society have much larger social networks and more regular social interactions as a by-product of work or school. For elderly members of society, often more isolated, the more basic social interactions in a retail setting are of greater significance to maintaining positive wellbeing. Robert Putman distinguishes between productive activities (doing things together) and consumptive activities (watching things together). Productive activities are better for creating social ties and feelings of social connectedness. For the elderly, social connectedness and social isolation are the biggest determining factors for mental health and wellbeing. This is where retail can have its greatest impact on public health, perhaps its greatest positive impact on society in general. Considering the size and financial resources of current ageing populations, providing store experiences that are inviting, engaging and active for older shoppers is a massive opportunity for retail brands.
Nice on the eye, good for the brain
Exciting new domains of research are merging psychology, cognitive neuroscience and design. While the relationship between the three is not yet clear, previous studies have found viewing art improves psychological and physiological states that enhance wellbeing. A 2006 study by Clow and Fredhoi found that visiting the Guildhall Art Gallery in London lowered participants salivary cortisol levels and (subjective) stress levels. Neuroaesthetics explains how aesthetic experiences can influence our wellbeing - simplified, viewing something that is visually pleasing leads to positive emotion by activating brain regions associated with reward and emotion processing.
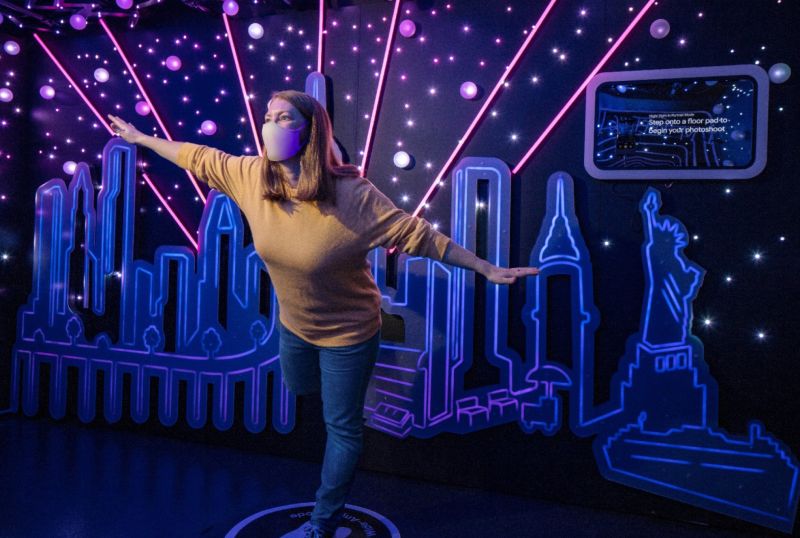
This sheds new light on the importance of aesthetics in retail store design. Can a visually pleasing store leave customers feeling more positive about their store experience? At the 2019 Salon del Mobile in Milan, an exhibition presented by Google measured physiological responses to three interior environments. Using wristbands to measure biometrics, it showed that visitors’ heart rate, skin conductivity, skin temperature, and breathing rate responded to design elements such as lighting, furnishing, colour, scent, and music. This begins to provide scientific evidence that retail designers can meaningfully use aesthetics to reduce stress or arouse a physiological response in a store environment.
The power of a self-actualising store experience
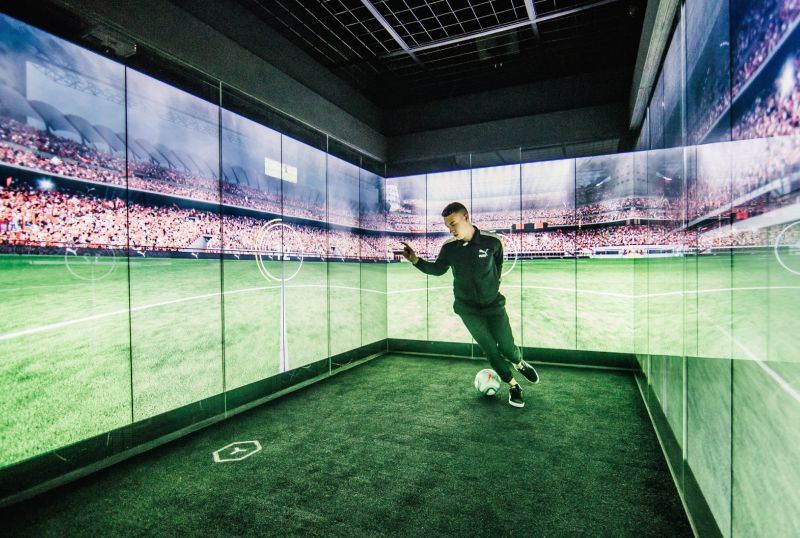
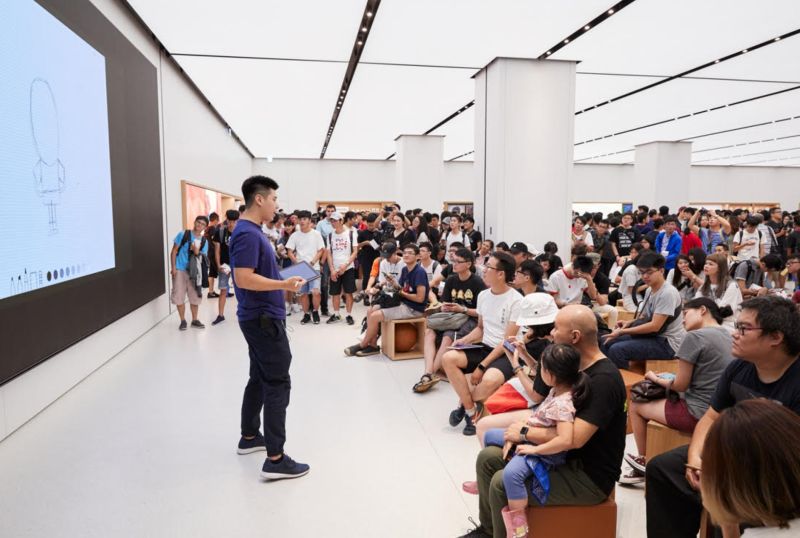
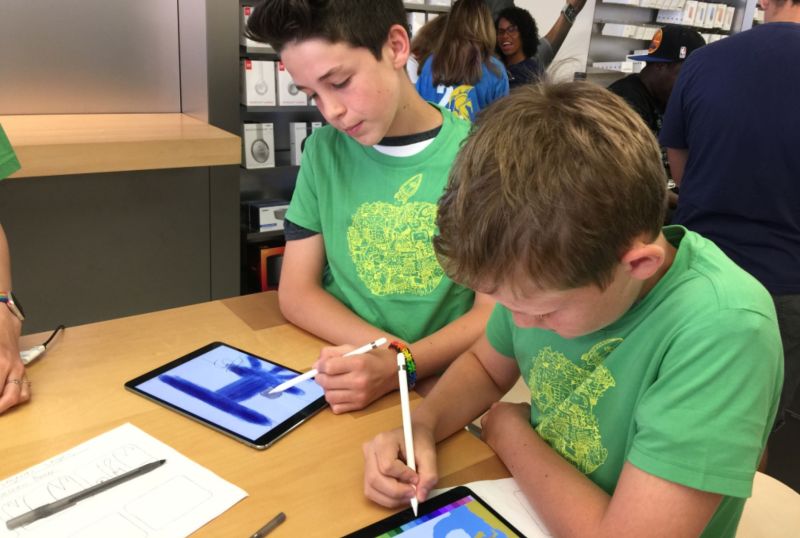
The field of positive psychology has established that being in a ‘flow’ state improves our wellbeing. A flow state refers to a mental state when we are immersed in an activity, focused, energised and aligned with the task at hand. It’s an active, meditative state where there is a balance between the skills of a person and the challenge of the activity with a clear goal in mind. How flow states influence our wellbeing should be front of mind when designing any person-centred experience, including retail.
Science journal Environment and Behaviour published a study analysing the daily experiences and wellbeing of 500 U.S. families, which found that individuals that had stronger ‘flow experiences’ in their leisure activities showed greater levels of wellbeing. Another study by the science journal Leisure Studies analysed the daily experiences of older adults and found that flow experiences and ‘serious leisure’ were associated with positive (affective) wellbeing. ‘Serious leisure’, in many ways similar to flow, was defined as activity demanding commitment, something that satisfies with personal or social rewards. Is it possible this is an insight into what can make the most rewarding retail experience? Perhaps rather than comfort, we seek a challenge and rather than service, we seek enrichment?
For brands, the most positive function of a store is to create an environment that facilitates and builds a relationship between customers and the brand. This is the ambitious goal of idealistic retail designers and businesses alike. Can retail experiences that encourage a state of ‘flow’ deliver this desired level of customer attachment to the brand? Research published in Frontiers in Psychology found that flow-induced activities also establish deep connections to the location that they take place in. We associate the feelings of personal growth, learning and development to that specific environment. The future of retail must take advantage of this.
The link between brand mission and an aligning self-identity is already understood by retail brands, for example, a person who passionately identifies as ecological will endorse or support a brand that is sustainable. The person’s association with the ecologically minded brand becomes self-affirming or even self-actualising. What’s missing in this dynamic is the integration of the physical store to enhance this consumer-brand association. A flow-inducing experience - a goal-orientated immersed activity - that embodies that brand mission could turn the physical retail experience into a self-actualising moment.
There is no universal experience for improving wellbeing
A store’s ability to be personalised and adaptable is incredibly relevant in the context of shopper wellbeing. There are numerous formulas to creating a retail experience that may contribute to improved wellbeing. Shoppers during the week, after work, might require detachment, escape or relaxation. While daytime shoppers, who may be more energetic and have a higher capacity to focus, might benefit from self-developing activities that are goal-oriented. Different brands will also attract varied customers with different needs or expectations. The needs of a teenage consumer visiting a flagship tech store will vary significantly to those of a parent and child visiting a toy store. An elderly customer may benefit more from an active social experience than an adolescent customer, but less from an activity that challenges them or pushes their limits. The customer circumstances, brand values and product offering must all be considered in identifying the ideal strategy to improve wellbeing. Brands and retail designers must understand who the customers are and what relationship they have with the brand.
Retailers should leverage these insights to stand out and to move their store past the transactional. Many of these insights suggest store objectives that are not new, but this understanding reaffirms the need to shift stores towards prioritising experiences instead of transactions. After understanding the possibilities of wellbeing in retail, the challenge is for designers to translate these broader strategies into design solutions. How does a store achieve flow experiences that integrate customer and brand missions? How do we design the right social or escapist experiences? The challenge also lies in the decision making that precedes design decisions. Are there designers bold enough to create experiences that are challenging rather than comfortable or convenient? Are there senior leaders in retail willing to make profound decisions to prioritise customer wellbeing in their store experiences? This new perspective on the physical store can be a reinvigorating mission for retail brands, a way to stand out among competitors and be a positive force for good. Focusing on customer wellness can act as a new way to create loyal connections and new brand ambassadors. There is no bigger issue than wellbeing, and as with other prominent social issues, retail has a duty to have a positive impact.